When shopping for an engagement ring or fine jewelry in 2025, you’re faced with more choices than ever before. The diamond landscape has evolved dramatically, with lab-grown diamonds now capturing significant market share alongside traditional natural diamonds. This comprehensive guide examines the fundamental differences, costs, ethical considerations, and practical factors to help you make an informed decision based on your values, budget, and lifestyle.

Whether you’re drawn to the billion-year journey of natural diamonds or the innovative technology behind lab-grown alternatives, understanding the nuances of each option is crucial for making a choice you’ll cherish for a lifetime.
What’s the Difference?
Chemical and Physical Properties
The most important fact to understand is that lab-grown diamonds and natural diamonds are chemically, physically, and optically identical. Both consist of pure carbon atoms arranged in the same crystal lattice structure, scoring a perfect 10 on the Mohs hardness scale. This means they exhibit the same brilliance, fire, and scintillation that make diamonds so captivating.
To the naked eye, even experienced jewelers cannot distinguish between natural and lab-grown diamonds. Both types can achieve exceptional clarity, color grades, and cut quality. The Federal Trade Commission has recognized lab-grown diamonds as “real diamonds” since 2018, requiring only that they be clearly identified as laboratory-created.
Formation and Origin
The primary difference lies in their origin story. Natural diamonds formed 1-3 billion years ago deep within the Earth’s mantle under extreme pressure and temperature conditions. They were brought to the surface through volcanic eruptions and are extracted through mining operations.
Lab-grown diamonds are created in controlled laboratory environments using two primary methods:
- High Pressure High Temperature (HPHT): Mimics natural formation conditions with extreme pressure and heat
- Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD): Uses carbon-rich gas that crystallizes layer by layer onto a diamond seed
The entire lab-grown process takes just 3-4 weeks, compared to the billions of years required for natural formation.

Detection Methods
Despite their identical properties, advanced scientific equipment can detect subtle differences between natural and lab-grown diamonds. Professional gemological laboratories use sophisticated instruments including photoluminescence spectroscopy and specialized microscopy to identify growth patterns and trace elements.
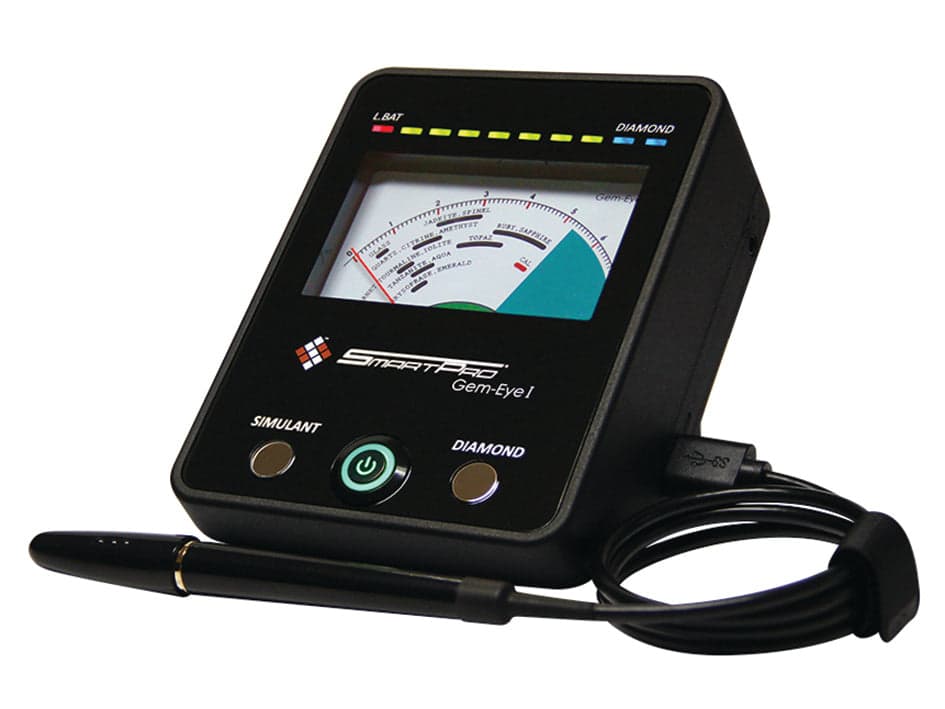

Thermal conductivity diamond testers, commonly used by jewelers, cannot distinguish between natural diamonds and lab-grown stones since both conduct heat identically. However, electrical conductivity testers can provide more accurate identification, as diamonds and diamond simulants like moissanite conduct electricity differently.
| Characteristic | Natural Diamonds | Lab-Grown Diamonds |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Pure Carbon (C) | Pure Carbon (C) |
| Physical Properties | Identical crystal structure | Identical crystal structure |
| Hardness (Mohs Scale) | 10 (Hardest natural material) | 10 (Same as natural) |
| Visual Appearance | Indistinguishable to naked eye | Indistinguishable to naked eye |
| Formation Time | 1-3 billion years | 3-4 weeks |
| Price per Carat (1ct, 2025) | $4,000 – $9,000 | $800 – $2,000 |
| Environmental Impact | High (mining, transportation) | Lower (controlled production) |
| Ethical Concerns | Potential conflict issues | Ethically sourced |
| Certification Available | GIA, IGI, HRD, AGS | GIA, IGI, HRD, AGS |
| Resale Value | 20-60% of retail price | 10-30% of retail price |
| Detection Method | Requires specialized equipment | Requires specialized equipment |
| Durability for Daily Wear | Excellent – built for centuries | Excellent – identical durability |
Price Breakdown in 2025
Current Market Pricing
The price differential between natural and lab-grown diamonds has widened significantly in 2025. Based on current market data, here’s what you can expect to pay per carat:
Natural Diamonds (1 carat): $4,000 – $9,000
Lab-Grown Diamonds (1 carat): $800 – $2,000
This represents savings of 60-85% when choosing lab-grown diamonds, with the exact discount varying based on the specific quality characteristics (cut, color, clarity, carat weight).
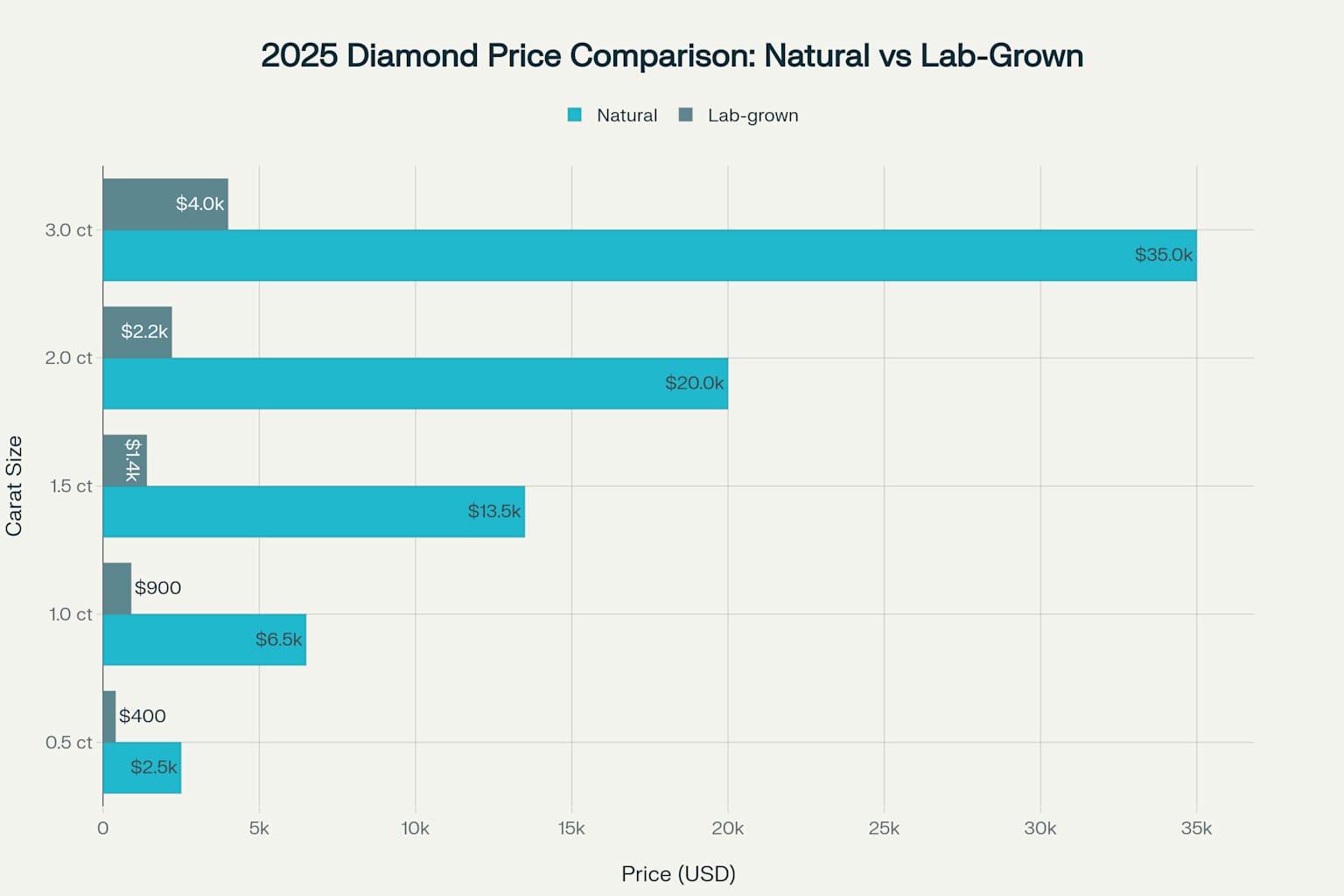
Why the Price Difference?
Several factors contribute to this substantial price gap:
Production Costs: Lab-grown diamonds avoid the extensive costs associated with mining, including exploration, extraction, transportation, and environmental remediation.
Scalability: Laboratory production can be scaled up more easily than discovering and developing new mines.
Market Perception: Natural diamonds command premium pricing due to their rarity and traditional luxury positioning.
Supply Dynamics: Lab-grown diamond production capacity continues to expand rapidly, while natural diamond mining output is declining.
Long-term Value Trends
Lab-grown diamond prices have dropped dramatically since 2020, falling by 70-80% as production technology improved and competition increased. This trend is expected to continue, potentially making lab-grown diamonds even more affordable in the coming years.
Ethical and Environmental Factors
Growing Consumer Consciousness
Modern consumers, particularly millennials and Gen Z, increasingly prioritize ethical and sustainable purchasing decisions. According to recent surveys, 78% of consumers say that knowing about a brand’s responsible business practices influences their purchasing decisions. Nearly half of respondents indicated they would pay significantly more for ethically sourced products.

Environmental Impact Comparison
Natural Diamond Mining:
- Requires moving approximately 1,750 tonnes of earth per carat
- Consumes 127 gallons of water per carat
- Generates 160-600 kg of CO₂ emissions per carat
- Can cause habitat destruction, soil erosion, and water pollution
Lab-Grown Diamonds:
- Produce 20-40 kg of CO₂ emissions per carat when using renewable energy
- Require significantly less water and land disruption
- Generate minimal waste compared to mining operations
- Some manufacturers achieve carbon-neutral production using renewable energy sources
Ethical Sourcing and Certification
The Kimberley Process remains the primary certification system for natural diamonds, preventing conflict diamonds from entering the legitimate trade. Established in 2003, it currently represents 99.8% of global rough diamond production across 86 countries.
However, critics argue that the Kimberley Process has limitations, as it only addresses conflict financing and doesn’t cover broader human rights issues, labor practices, or environmental concerns.
For consumers seeking ethical engagement ring options, lab-grown diamonds offer a clear alternative, as they avoid the complex supply chain issues associated with mining.
Certification and Quality
Understanding Diamond Certifications
Both natural and lab-grown diamonds can receive certification from the same reputable gemological institutions. The major certification bodies include:
GIA (Gemological Institute of America): Widely regarded as the gold standard with the strictest grading standards. GIA created the 4Cs grading system and maintains consistent, conservative grading practices.
IGI (International Gemological Institute): The largest certification body globally, particularly popular for lab-grown diamonds. IGI provides comprehensive reports and is generally considered reliable, though historically slightly more lenient than GIA.
HRD (Hoge Raad voor Diamant): The Diamond High Council offers high-quality certification with standards comparable to GIA.
AGS (American Gem Society): Known for specialized cut grading and ethical business practices.
GIA vs IGI: Which Is Better?
The choice between GIA and IGI certification often comes down to the specific diamond type and your priorities:
GIA Advantages:
- Most prestigious and globally recognized
- Strictest, most consistent grading standards
- Higher resale value recognition
- Comprehensive research and education resources
IGI Advantages:
- Leading certifier for lab-grown diamonds
- More detailed reports for lab-grown stones
- Generally faster turnaround times
- Lower certification costs
For lab-grown diamonds specifically, IGI has become the industry standard, providing detailed information about the growth method and characteristics. Many retailers and consumers find IGI certification perfectly adequate for lab-grown stones, while GIA maintains its premium position for natural diamonds.
Reading Diamond Certificates
Modern diamond certificates include detailed information about:
- The 4Cs: Cut, Color, Clarity, and Carat weight
- Fluorescence characteristics
- Detailed plotting of inclusions and blemishes
- Proportions and symmetry grades
- Origin identification (natural vs. lab-grown)
- Security features and unique identification numbers
Which One Is Right for Your Engagement Ring?
Durability and Daily Wear
Both natural and lab-grown diamonds offer identical durability for engagement rings. With a hardness rating of 10 on the Mohs scale, both types can withstand daily wear for decades. The key durability factors are actually related to the ring setting and maintenance rather than the diamond type.

Emotional and Symbolic Value
The emotional significance of an engagement ring often depends on personal values and what the diamond represents to you:
Natural Diamond Appeal:
- Unique billion-year formation story
- Traditional luxury and prestige associations
- Rarity and connection to Earth’s geological history
- Potential family heirloom value
Lab-Grown Diamond Appeal:
- Represents innovation and modern values
- Alignment with sustainability and ethical principles
- Ability to afford larger or higher-quality stones within budget
- Focus on the relationship rather than traditional luxury markers
Resale Value Considerations
Natural diamonds typically retain 20-60% of their retail value in the resale market, while lab-grown diamonds often command only 10-30% of their original price. However, this shouldn’t be the primary consideration for engagement rings, as most couples purchase them as symbols of commitment rather than investments.
Current Trends and Social Acceptance
- 55% of US engagement rings now feature lab-grown diamonds (up from 2% in 2018)
- Millennials and Gen Z drive the shift toward sustainable options
- Customization and personalization increasingly important
- Alternative gemstones gaining popularity alongside both diamond types
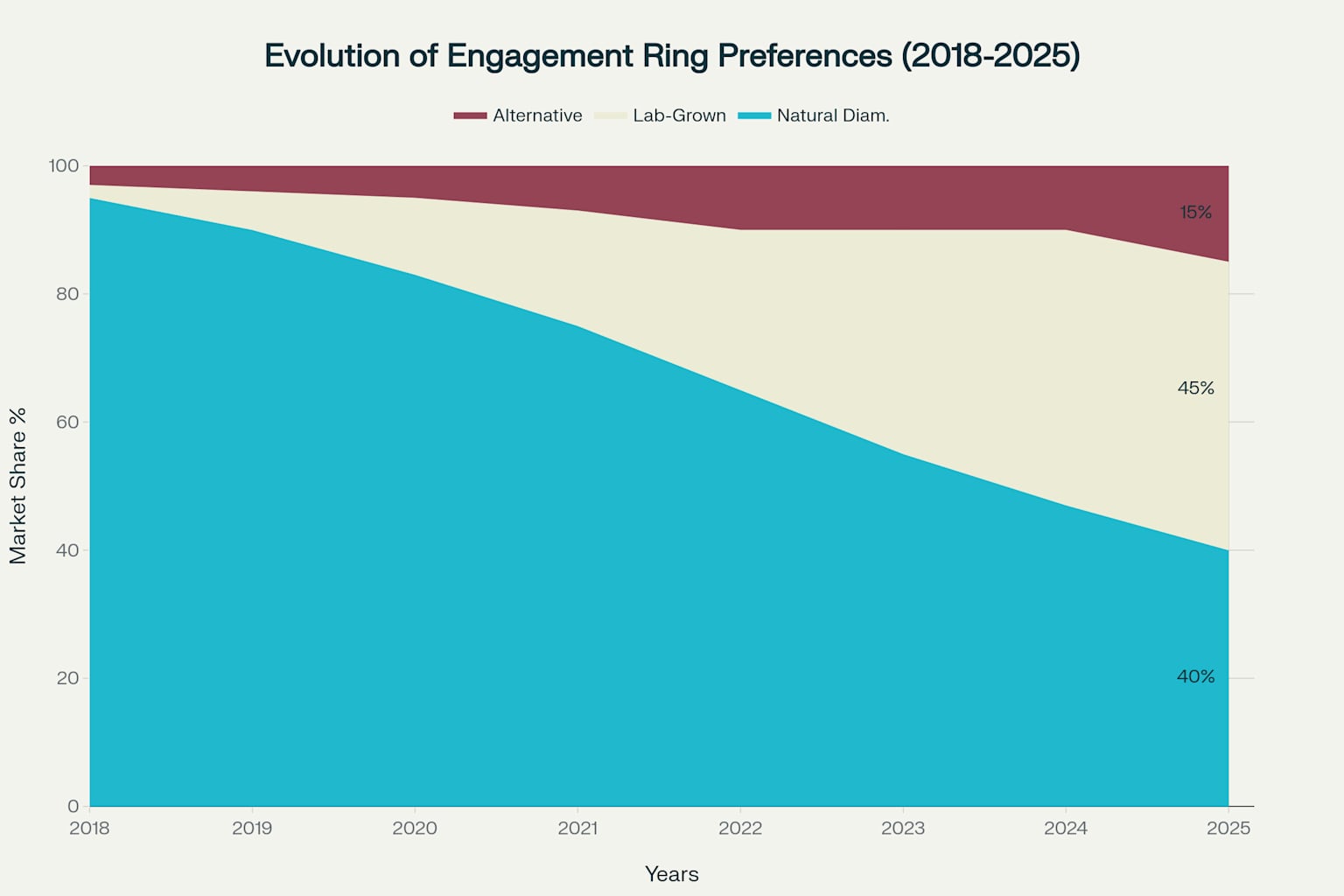
The social acceptance of lab-grown diamonds has reached a tipping point, with most consumers now viewing them as legitimate alternatives to natural stones.
Market Outlook: Next 5 Years
Production and Supply Trends
Lab-Grown Diamond Production:
- Market expected to reach $74-98 billion by 2030
- Production capacity expanding rapidly, especially in Asia
- Continued price declines anticipated as technology improves
- Quality improvements enabling larger, higher-grade stones
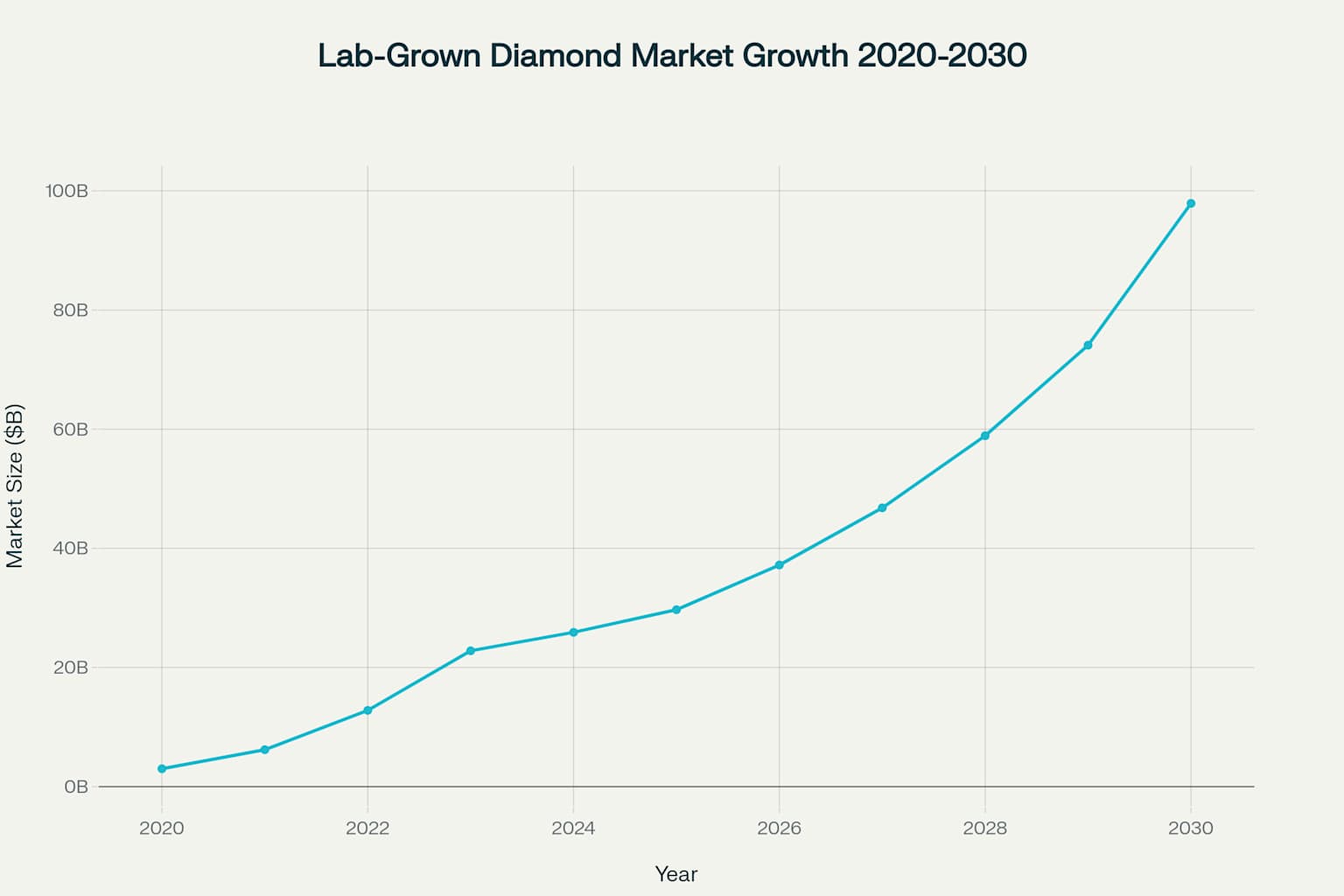
Natural Diamond Supply:
- Global mining output at lowest levels since 1995 (105 million carats)
- Major mines reaching end-of-life with limited new discoveries
- De Beers and other major producers cutting production
- Supply constraints likely to support pricing
Investment and Pricing Outlook
Natural Diamonds:
- Rare, high-quality stones may appreciate due to supply constraints
- Fancy colored diamonds showing strong investment potential
- Mass market stones may face continued pressure from lab-grown alternatives
Lab-Grown Diamonds:
- Continued price declines expected, particularly for larger stones
- Technology improvements driving cost efficiencies
- Market consolidation anticipated as production scales
Industry experts predict a two-tier market will develop, with natural diamonds maintaining premium positioning for luxury and investment pieces, while lab-grown diamonds dominate the broader consumer market.
Lab-Grown Diamonds Pros and Cons
When evaluating lab-grown diamonds pros and cons for your purchase decision, consider these key factors:
Advantages:
- Cost Savings: 60-85% less expensive than natural diamonds
- Ethical Sourcing: Avoid potential conflict diamond issues
- Environmental Benefits: Lower carbon footprint and no mining impact
- Quality Control: Consistent high quality due to controlled production
- Availability: Wide selection of sizes, colors, and qualities
Disadvantages:
- Lower Resale Value: Typically 10-30% of purchase price vs. 20-60% for natural
- Newer Technology: Less long-term market track record
- Potential Oversupply: Increasing production may further depress values
- Traditional Preferences: Some consumers still prefer natural diamonds’ heritage
Real Diamond vs Moissanite: Understanding Alternatives
While comparing real diamond vs moissanite options, it’s important to understand that moissanite is chemically different from both natural and lab-grown diamonds. Moissanite consists of silicon carbide rather than pure carbon, resulting in:
- Higher refractive index creating more “rainbow fire” than diamonds
- Slightly lower hardness (9.25 vs. 10 on Mohs scale)
- Significantly lower cost than both diamond types
- Different optical properties detectable by professionals
For those specifically seeking diamond alternatives, lab-grown diamonds offer true diamond properties at reduced cost, while moissanite provides a distinct gemstone option with its own unique characteristics.
Conclusion: Making Your Choice
Choosing between natural and lab-grown diamonds in 2025 ultimately depends on your personal values, budget, and priorities. Both options offer identical beauty, durability, and quality for engagement rings and fine jewelry.

Choose natural diamonds if you:
- Value traditional luxury and rarity
- Prioritize potential resale value
- Want the billion-year geological story
- Are purchasing larger investment-grade stones
Choose lab-grown diamonds if you:
- Want maximum value for your budget
- Prioritize ethical and environmental considerations
- Appreciate modern innovation and technology
- Plan to focus on ring design and overall aesthetics
The diamond industry has evolved to offer authentic choices that reflect diverse values and preferences. Whether you choose natural or lab-grown, ensure you work with reputable dealers, verify proper certification from recognized gemological institutes, and select a diamond that resonates with your personal story.
Still Not Sure? Here’s a Checklist to Help You Choose the Right Diamond for Your Lifestyle:
Budget Considerations:
- Determine your total budget for the ring
- Calculate whether lab-grown savings could upgrade other aspects (setting, size, quality)
- Consider long-term financial priorities
Values and Ethics:
- Research the importance of environmental impact to your decision
- Evaluate ethical sourcing priorities
- Consider what the diamond’s origin story means to you
Quality and Certification:
- Decide between GIA and IGI certification based on your priorities
- Understand the 4Cs and which aspects matter most to you
- Verify the reputation of your chosen retailer
Long-term Perspective:
- Consider your feelings about resale value vs. symbolic value
- Think about potential family heirloom considerations
- Evaluate your comfort with newer vs. traditional technology
By carefully considering these factors and the comprehensive information provided in this guide, you’ll be well-equipped to make a diamond choice that aligns with your values, budget, and vision for your perfect engagement ring or jewelry piece.
